Welcome to the official website of Dongguan Zeming — the leading factory for Bakelite molds and Bakelite processing!
Welcome to the official website of Dongguan Zeming — the leading factory for Bakelite molds and Bakelite processing!
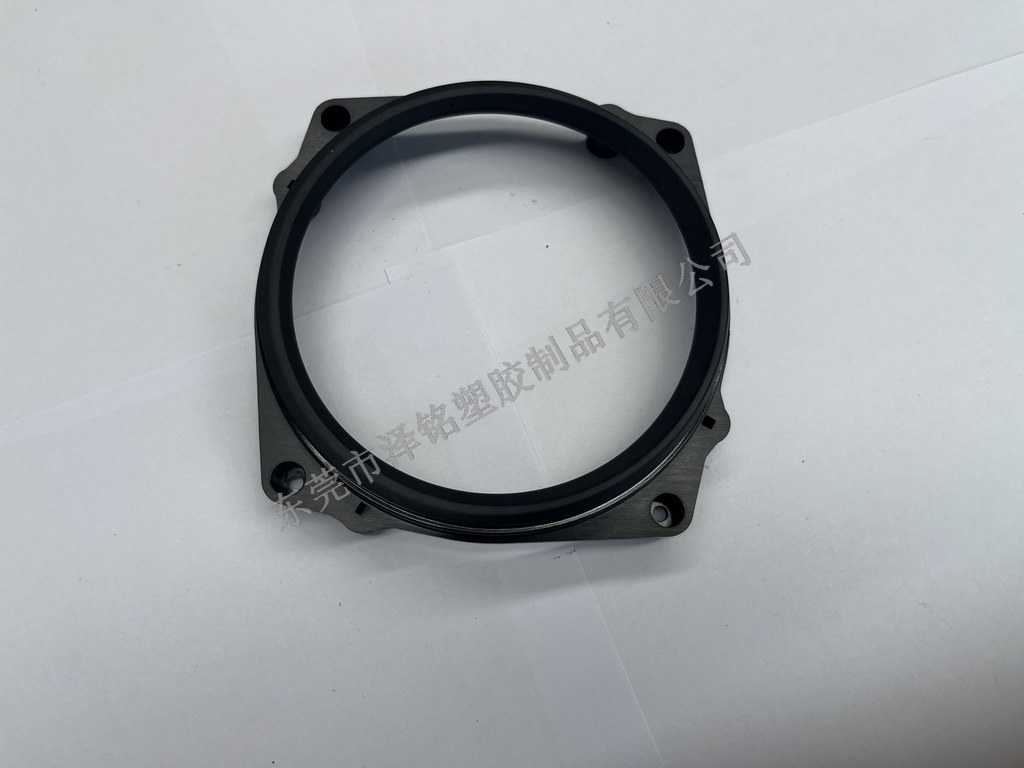
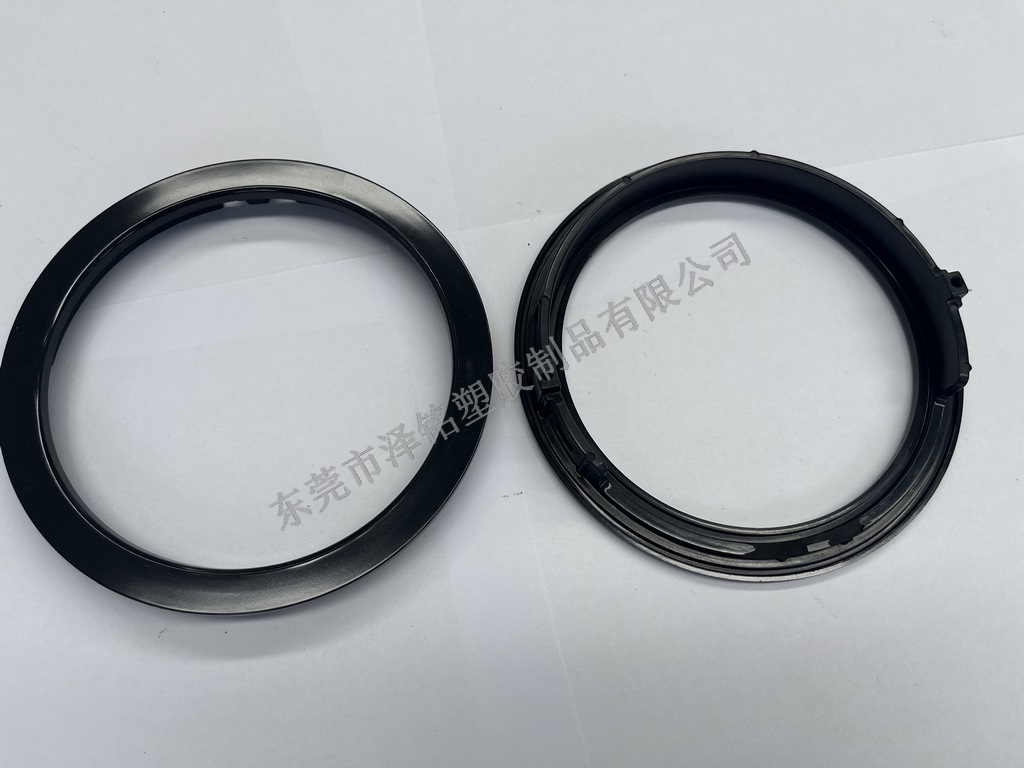
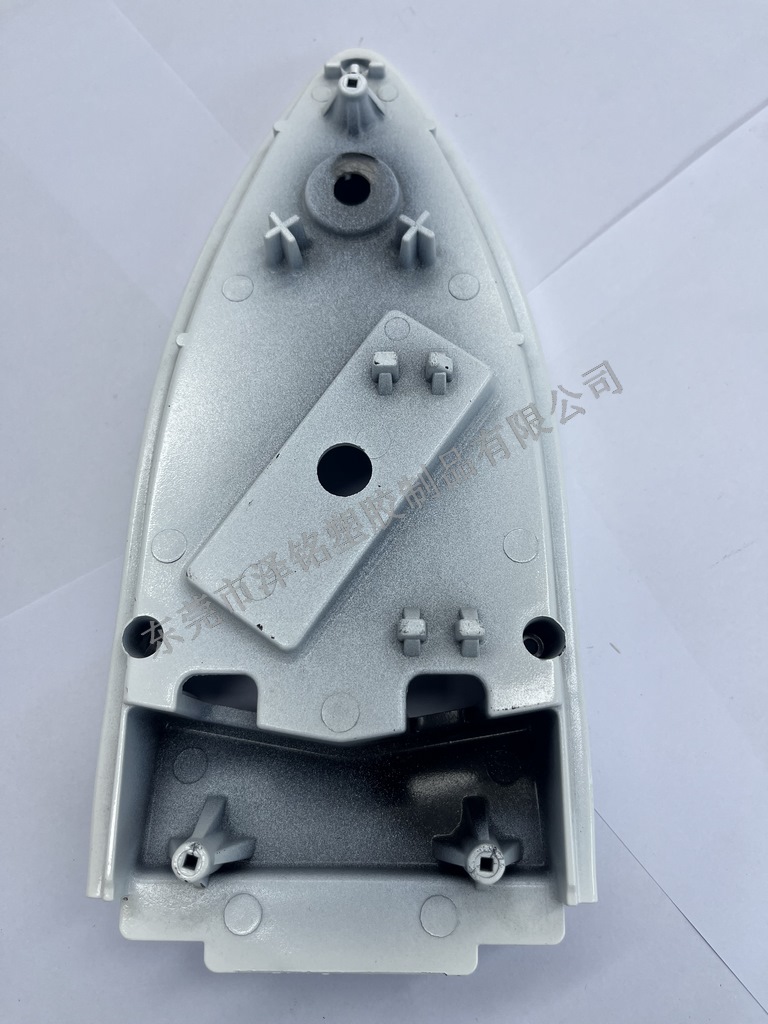
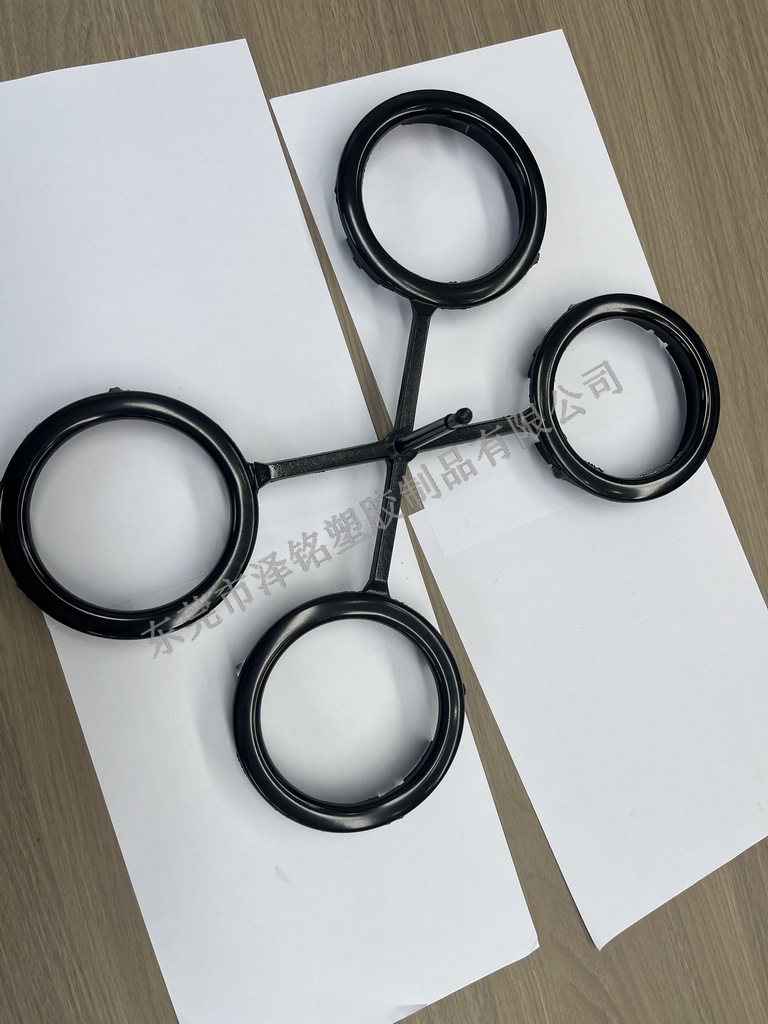
Zeming products meet international quality standards
Mold steel is all imported per customer requirements. Certified ISO9001:2015, tested for aging — mold life exceeds 500,000 cycles.

Zeming owns high‑precision detection equipment and automated robots. Full 2D & 3D inspection ensures precision within 0.01 mm.
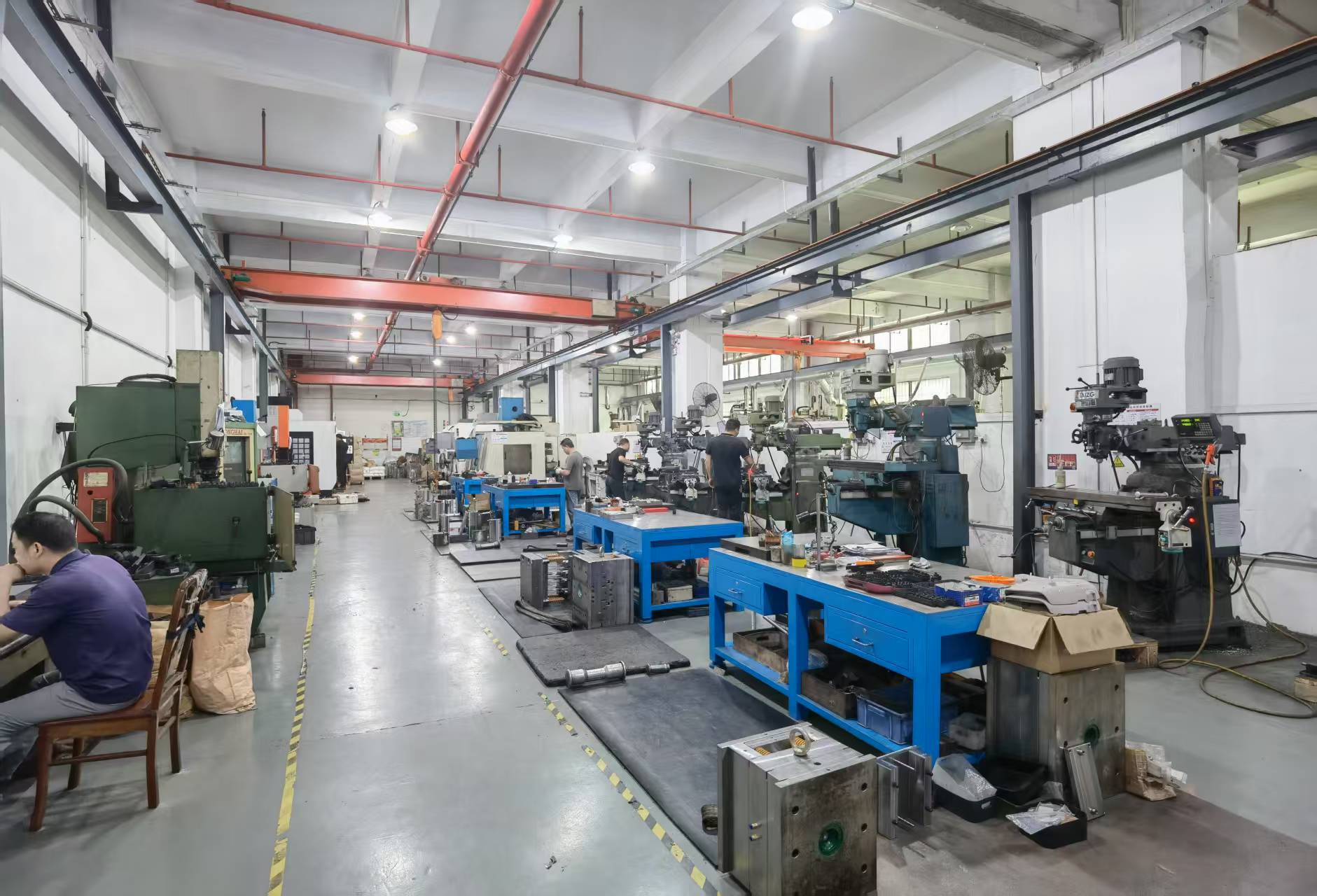

After molding, plastic (Bakelite) samples undergo three rounds of testing (high-temp, high-pressure, insulation) to meet customer requirements before mass production.

Zeming integrates design, R&D, manufacturing, and sales — providing 10+ color options under strict quality control to enhance product aesthetics.
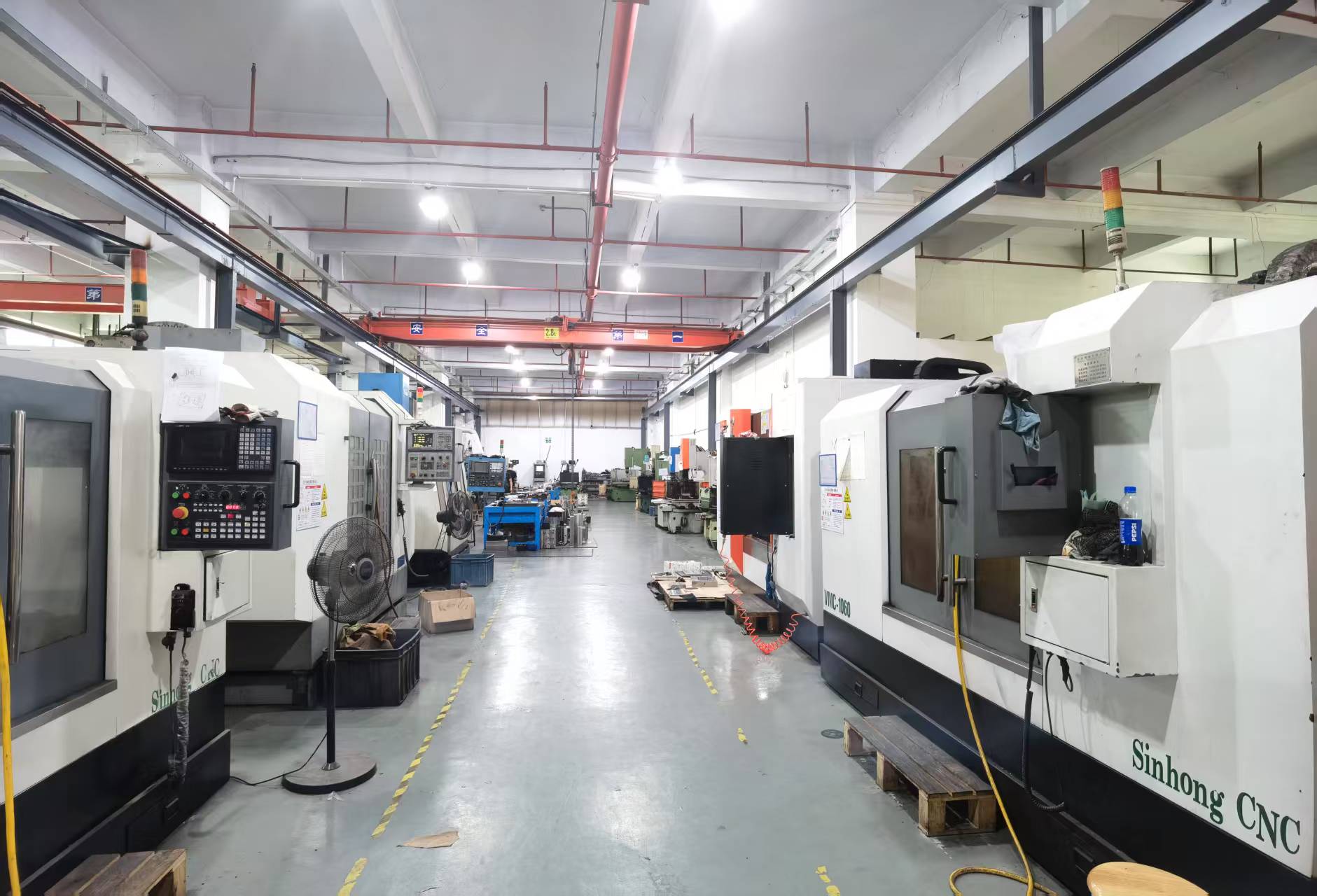

Customers are welcome to visit the factory for on‑site inspection
Served 900+ customers cumulatively
Fully imported high‑precision equipment, rigorous quality control

Factory includes engineering, tooling, thermoset molding, thermoplastic molding, QC, materials departments, etc.
“6S” international factory management system, audited by major Japanese brands
Strong R&D capability supporting custom development. Core R&D team has 10+ years’ experience.
View Factory Tour
Zeming has a comprehensive product quality management system,ISO9001 Quality Certification obtained
Partnering with multiple stable, high-quality material suppliers,Strict quality & cost control on procurement
Experienced production technicians,80% have over 3 years operation experience
Consult Now
Zeming owns high‑precision detection devices and automated robots
Equipped with full inspection facility, including 2D, 3D systems, ensuring strict control over details
Visit the Factory
Pre‑sale: Free structural design analysis
During‑sale: One‑on‑one tracking; production status updated anytime
After‑sale: Professional support, 24h standby; solution provided within 8h
Apply After‑salesTwo‑storey, 3,000+ sqm 6S factory base. Customers welcome to visit.

Founded in 2001, Zeming has over 20 years of experience in R&D and processing of thermoset and thermoplastic molds and injection molding. Located at No.1 Longshun Rd, Longjiantian, Huangjiang, Dongguan—a beautiful and accessible site with a complete supply chain. We have 100+ employees including engineers, production and quality staff, forming a comprehensive management team. Adhering to “customer first, quality above all, continuous improvement,” we are committed to offering premium plastic (thermoset, thermoplastic) products and professional services. We look forward to win‑win cooperation.
View MoreOne‑on‑one follow‑up, production status in your hands
Drawing Review
01
Sign Contract
02
Mold Design
03
Sign Injection Design
04
Mold Assembly
05
Mold Trial Production
06
Dimensional Inspection
07
Qualified Delivery
08
Manufacturing
09
Injection Production
1024‑year strong factory, clients worldwide
Plastic is a material mainly composed of high molecular weight synthetic resin, which can be molded into a certain shape under certain conditions (such as temperature, pressure, etc.) and maintain its shape at room temperature.
Plastics can be divided into two categories based on their surface properties after heating: thermosetting plastics and thermoplastic plastics. The characteristic of the former is that it undergoes a chemical reaction and hardens after being heated, pressurized, or treated with a hardening agent for a certain period of time at a certain temperature. After hardening, the chemical structure of the plastic changes, the texture becomes hard, insoluble in solvents, and no longer softens when heated. If the temperature is too high, it will decompose. The characteristic of the latter is that it undergoes a change in state after being heated, softening or melting from a solid into a viscous fluid state, but it can harden into a solid after cooling, and the process can be repeated multiple times, while the molecular structure of the plastic itself does not change.
Plastic is composed of synthetic resin as the basic raw material, and various auxiliary materials such as fillers, plasticizers, dyes, stabilizers, etc. are added. Therefore, different varieties and grades of plastics have different properties, compositions, ratios, and plastic production processes due to the use of resins and auxiliary materials, resulting in varying usage and process characteristics
Same. When designing this mold, it is necessary to understand the process characteristics of the plastic used.
The commonly used thermosetting plastics in the first section include phenol formaldehyde, amino (melamine, urea formaldehyde) polyester, and poly (ethylene propylene phthalate). Mainly used for compression molding, extrusion molding, and injection molding. Silicone, epoxy resin and other plastics are currently mainly used for low-pressure extrusion packaging of electronic components and casting molding.
1、 Process characteristics (1) Shrinkage rate: The performance of plastic parts that undergo dimensional shrinkage after being removed from the mold and cooled to room temperature is called shrinkage. Due to the fact that shrinkage is not only the thermal expansion and contraction of the resin itself, but also related to various forming factors, the shrinkage of the formed plastic part should be referred to as forming shrinkage.
1. The forms of forming shrinkage are mainly manifested in the following aspects:
(1) The linear shrinkage of plastic parts is caused by thermal expansion and contraction, as well as elastic recovery and plastic deformation during demolding, resulting in a reduction in size after cooling to room temperature. Therefore, compensation must be considered in the design of the mold cavity.
(2) During directional shrinkage forming, molecules are arranged in a directional manner, resulting in anisotropy of the plastic part. Along the direction of the material flow (i.e. parallel direction), the shrinkage is greater and the strength is higher, while in the direction perpendicular to the material flow (i.e. perpendicular direction), the shrinkage is smaller and the strength is lower. In addition, due to uneven density and filler distribution in various parts of the plastic part during forming, the shrinkage is also uneven. The occurrence of shrinkage differences makes plastic parts prone to warping, deformation, and cracking, especially during extrusion and injection molding where directionality is more pronounced. Therefore, when designing the mold, the shrinkage directionality should be considered, and the shrinkage rate should be selected according to the shape of the plastic part and the flow direction.
(3) During the formation of post shrinkage plastic parts, a series of stresses are caused by factors such as forming pressure, shear stress, anisotropy, uneven density, uneven distribution of fillers, uneven mold temperature, uneven hardening, and plastic deformation. These stresses cannot be completely eliminated in the viscous flow state, resulting in residual stresses during the formation of plastic parts under stress conditions. After demolding, due to the influence of stress balance and storage conditions, the residual stress changes and the plastic part undergoes further shrinkage, which is called post shrinkage. Generally, plastic parts undergo the greatest changes within 10 hours after demolding, and are basically set after 24 hours. However, the final stability takes 30-60 days. Generally, the post shrinkage of thermoplastic is greater than that of thermosetting, and extrusion and injection molding are greater than compression molding.
(4) Post processing shrinkage sometimes requires heat treatment of plastic parts after forming according to performance and process requirements, which can also cause changes in the size of the plastic parts. Therefore, when designing molds for high-precision plastic parts, the errors caused by post shrinkage and post-processing shrinkage should be considered and compensated for. 2. The shrinkage rate can be used to calculate the forming shrinkage of plastic parts, as shown in formulas (1-1) and (1-2).
(1-1) Q real=(a-b)/b × 100 (1-2) Q counter=(c-b)/b × 100
In the formula: Qreal - actual shrinkage rate (%)
Q meter - Calculate shrinkage rate (%)
A - Unidirectional dimension of plastic parts at forming temperature (mm)
B - Unidirectional dimension of plastic parts at room temperature (mm)
C - Unidirectional dimension of mold at room temperature (mm)
The actual shrinkage rate represents the actual shrinkage that occurs in the plastic part. As its value differs very little from the calculated shrinkage, Q is used as the design parameter to calculate the cavity and core dimensions during mold design. 3. The factors that affect the change in shrinkage rate are not only different for different types of plastics during actual forming, but also for different batches of the same type of plastic or different parts of the same plastic part. The main factors that affect the change in shrinkage rate are as follows.
(1) Various types of plastics have their own shrinkage ranges, and the shrinkage rate and anisotropy of the same type of plastic vary due to differences in fillers, molecular weights, and ratios.
(2) The shape, size, wall thickness, presence or absence of inserts, as well as the number and layout of inserts, have a significant impact on the shrinkage rate of plastic parts.
(3) The parting surface and pressure direction of the mold structure mold, as well as the form, layout, and size of the pouring system, also have a significant impact on the shrinkage rate and directionality, especially in extrusion and injection molding.
(4) The extrusion and injection molding processes generally have a large shrinkage rate and obvious directionality. Preheating conditions, forming temperature, forming pressure, holding time, filling material form, and hardening uniformity all have an impact on shrinkage rate and directionality.
As mentioned above, when designing the mold, the shrinkage rate range provided in the instructions of various plastics should be considered, and the shrinkage rate value should be selected comprehensively based on various factors such as the shape, size, wall thickness, presence or absence of embedded parts, parting surface and pressure forming direction, mold structure and feeding port form, size and position, forming process, etc. of the plastic part. When it comes to extrusion or injection molding, it is often necessary to select different shrinkage rates based on the shape, size, wall thickness, and other characteristics of each part of the plastic part.
In addition, forming shrinkage is also influenced by various forming factors, but mainly determined by the type of plastic, the shape and size of the plastic part. So adjusting various forming conditions during forming can also appropriately change the shrinkage of the plastic part.
(2) Liquidity
The ability of plastic to fill the cavity at a certain temperature and pressure is called fluidity. This is an important process parameter that must be considered in mold design. High fluidity can easily cause excessive material overflow, incomplete filling of the mold cavity, loose plastic structure, resin and filler accumulation separately, easy mold sticking, difficult demolding and cleaning, premature hardening and other drawbacks. But if the liquidity is small, the filling is insufficient, it is difficult to form, and the forming pressure is high. So the flowability of the selected plastic must be compatible with the requirements of the plastic part, forming process, and forming conditions. When designing molds, the pouring system, parting surface, and feeding direction should be considered based on the flow performance. The flowability of thermosetting plastics is usually expressed in terms of Raschig flowability (measured in millimeters). The larger the value, the better the fluidity. Each variety of plastic is usually divided into three different levels of fluidity for different plastic parts and forming processes to choose from. When the complex shape of plastic parts with large surface area, multiple inserts, thin and weak cores and inserts, narrow deep grooves, and thin walls is not conducive to filling, plastic with good flowability should be used. Plastic with a flowability of at least 150mm should be used for extrusion molding, while plastic with a flowability of at least 200mm should be used for injection molding. In order to ensure that each batch of plastic has the same fluidity, the co batch method is commonly used in practice to adjust, that is, to match plastics of the same variety with different flowability, so that the flowability of each batch of plastics compensates for each other, in order to ensure the quality of plastic parts. The Raschig flowability values of commonly used plastics are detailed in Table 1-1, but it must be pointed out that the injectability of plastics is not only determined by the type of plastic, but also often affected by various factors during the filling of the mold cavity, resulting in changes in the actual ability of plastics to fill the mold cavity. If the particle size is fine and uniform (especially for round granules), the humidity is high, the moisture and volatile substances are abundant, the preheating and forming conditions are appropriate, the surface smoothness of the mold is good, and the mold structure is appropriate, all of which are conducive to improving fluidity. On the contrary, poor preheating or forming conditions, poor mold structure, high flow resistance, long or expired plastic storage period, high storage temperature (especially for amino plastics), etc. can all lead to a decrease in the actual flow performance of plastic filling the mold cavity, resulting in poor filling.
(3) Specific volume and compression ratio
The specific volume is the volume occupied by each gram of plastic (measured in cubic centimeters per gram). The compression ratio is the ratio of the volume or specific volume of the plastic powder to the plastic part (which is always greater than 1). They can all be used to determine the size of the mold loading chamber. A large value requires a large volume of the loading chamber, while also indicating that there is a lot of inflation inside the plastic powder, making it difficult to exhaust, resulting in a long forming cycle and low productivity. If the specific volume is small, the opposite is true, and it is beneficial for pressing and compacting. The specific capacities of various plastics are detailed in Table 1-1. However, the specific volume value is often subject to errors due to the particle size and unevenness of the plastic.
(4) Hardening characteristics
Thermosetting plastics transform into a plastic viscous flow state under heating and pressure during the forming process, increasing their flowability and filling the mold cavity. At the same time, condensation reactions occur, increasing cross-linking density and rapidly decreasing flowability. The melt gradually solidifies. When designing molds, attention should be paid to the ease of loading, loading and unloading of inserts, and selection of reasonable forming conditions and operations for materials with fast hardening speed and short flow state to avoid premature hardening or insufficient hardening, which may lead to poor plastic forming.
The hardening speed can generally be analyzed from the holding time, which is related to the type of plastic, wall thickness, shape of the plastic part, and mold temperature. But it is also affected by other factors, especially related to the preheating state. Proper preheating should be maintained under conditions that allow the plastic to exert maximum fluidity, and the hardening speed should be maximized. Generally, if the preheating temperature is high and the time is long (within the allowable range), the hardening speed will be accelerated, especially if the pre pressed ingot billet is preheated at high frequency, the hardening speed will be significantly accelerated.
In addition, the hardening speed increases with high forming temperature and long pressing time. Therefore, the hardening speed can also be appropriately controlled by adjusting the preheating or forming conditions.
The hardening speed should also be suitable for the requirements of the forming method. For example, during injection molding and extrusion molding, slow chemical reactions and hardening should be required during plasticization and filling, and a relatively long flow state should be maintained. However, after filling the mold cavity, it should harden quickly under high temperature and high pressure.
(5) Moisture and volatile matter content
Various plastics contain varying degrees of moisture and volatile matter content, which can increase flowability, cause material overflow, maintain for a long time, cause shrinkage, and lead to problems such as ripples and warping, affecting the mechanical and electrical properties of plastic parts. But when the plastic is too dry, it can also lead to poor fluidity and difficulty in forming. Therefore, different plastics should be preheated and dried according to requirements. For materials with strong moisture absorption, especially in humid seasons, even preheated materials should be prevented from absorbing moisture again.
Due to the presence of different components of moisture and volatile compounds in various plastics, and the condensation of moisture during the condensation reaction, these components need to be transformed into gases during molding and discharged outside the mold. Some gases have a corrosive effect on the mold and a stimulating effect on the human body. Therefore, in mold design, it is necessary to understand the characteristics of various plastics and take corresponding measures, such as preheating, chrome plating on the mold, opening exhaust slots, or setting exhaust processes during forming.
2、 Forming characteristics
In mold design, it is necessary to master the forming characteristics of the plastic used and the process characteristics during forming.
1. The process characteristics of commonly used thermosetting plastics are shown in Table 1-1
2. The forming characteristics of commonly used thermosetting plastics are shown in Table 1-2. The forming characteristics of various plastics are not only related to the types of plastics, but also to the types and particle sizes of the fillers contained, as well as the uniformity of the particles. Fine materials have good flowability, but preheating is not easy to achieve uniformity, filling with air is difficult to discharge, heat transfer is poor, and forming time is long.
Coarse plastic parts lack luster and are prone to surface unevenness. Being too coarse or too fine directly affects the specific volume and compression rate, as well as the volume of the mold feeding chamber. Uneven particles result in poor formability and uneven hardening, and it is not advisable to use volumetric feeding method
Precautions for using hot runner system in Guangdong Plastic Mold Factory
In the design and manufacturing of plastic molds, some molds require the use of hot runner systems. What should be noted when using runners?
Precautions for using hot runner system in Guangdong Plastic Mold Factory
1. The channel is heated externally and hot spots are considered to be removed from the design (for example, four heaters are symmetrically placed around the flow channel).
To ensure proper heating of the manifold, use at least 50 watts per cubic inch of steel and evenly distribute the heater on the manifold.
3. The manifold channel should be at least 0.50 inches (12.7 millimeters). The production of large parts and long flow lengths requires larger diameters.
4. Each channel should be designed as a streamline with no dead corners for material suspension or disassembly. There is a protruding plug at the corner.
To maintain temperature consistency, it is recommended to use voltage proportional temperature control.
6. The spout should be short and straight, exceeding 6 inches in length, and equipped with two temperature control zones.
7. The manifold dividing joint and punching nozzle should be insulated appropriately from the clamping steel plate. There is a 0.03 inch (0.79 mm) air gap between the two to reduce metal surface connections, and stainless steel or titanium support pads are used.
8. The injection tube has an external heater that reaches or exceeds the mold hole at least.
9. Each injection port has a separate sealing ring controller.
10. The resin melt temperature of the manifold and punching tube is the same as the melt temperature of the tube.
11. The insulation material flow channel system is not suitable for engineering thermoplastic plastics.
12. For ULTRAM resin, the inherent mold area will produce stripes during production, so it is necessary to know what special valve gate hot runner system needs to be used.
Temperature control of molds in Guangdong Plastic Mold Factory
Proper control of the surface temperature of the core and cavity is crucial for the production of parts in plastic mold factories. Now let's take a look at how I control the temperature of plastic molds.
In order to independently control half of the temperature of the mold, dual zone or separate controllers are usually required. Unified mold temperature control is crucial for extending cycle time and effectively controlling component tolerances. For large hollow or core shapes, it is usually recommended to keep the temperature difference of steel below 20f (-7c) and small parts below 5f (-15c). The stricter the control, the greater the degree of freedom in processing. Cooling channels larger than 12.7 millimeters (1/2 inch), 38~50.8 millimeters (1-1/2 inch~2 inch), are 1/2 inch larger than the hollow and core surfaces. Correct temperature regulation ensures uniform heating of the mold surface. The huge temperature difference on the surface of the mold leads to different cooling rates, resulting in injection stress on the product. For the same reason, the temperature difference between the core and the cavity usually does not exceed 40F (C2C).
Dongguan plastic mold is a compact tool that has a messy shape and can withstand the expansion force of the blank. Therefore, there are high requirements for structural strength, stiffness, general hardness, general roughness, and machining accuracy. The increase of plastic molds in Dongguan is one of the important indicators of the degree of mechanical manufacturing, with long cycles and high processing costs (especially for compact and messy plastic molds or large plastic molds).
After long-term operation, Dongguan plastic molds need to be polished sharp, and the sharp blades should be demagnetized and not magnetized, otherwise it is easy to cause blockage. Plastic mold operating enterprises should keep detailed records, including their operations, maintenance (lubrication, cleaning, rust prevention), and damage to the environment. They should also provide information based on damaged parts and wear levels for reference and use. The data and molding process parameters of plastic molds and materials used in the product can shorten the trial operation time of plastic molds and improve cross production efficiency.
The combined Dongguan plastic mold consists of compression molding, extrusion molding, injection molding, blow molding, and low foaming. Plastic molds mainly include cavities that are combined with the bottom plate of the concave mold, as well as card plates that are combined with the concave mold components and concave molds. A concave die is a type of variable core convex die, consisting of a convex die combination bottom plate, a convex die part, a convex die combination card plate, a cavity cutting part, and a side cutting combination plate.
The coordinated changes of convex mold, concave mold, and auxiliary molding system can process a series of plastic parts with different shapes and sizes. In the plastic processing industry, it is used in conjunction with plastic molding machines to provide complete equipment and cutting tools for plastic products. Due to the diversity of plastics and processing methods, as well as the messy and simple structure of plastic molding machines and plastic products, there are also various types and structures of plastic molds in Dongguan.
The choice of plastic mold steel in Guangdong is that there is no "universal" cast steel for plastic molds, but P-20 steel is considered a multi-purpose steel in industry. Below, the editor will introduce P-20 steel, which is pre hardened to RC 30-32 state and is very hard, but it is also quite easy to process. When the cavity size exceeds 12 × 12 × 12 inches, the P-20 steel that needs to be considered has a mold cycle of 500.
Selection and Introduction of Plastic Mold Steel in Guangdong
When manufacturing plastic molds and steel molds, sliders, elevators, other diagonal pins, and moving parts are required. It is recommended to use various alloys and hardness steels to reduce wear or high adhesion wear. The common method for manufacturing large plastic mold steel molds is to use H-13 steel sliders or elevators that have been heat-treated to RC50-52 hardness, or to use partially friction steel surfaces with hardness in the range of RC 55-RC 58.
The correct gate position for Guangdong plastic mold steel
Designers should not only pay special attention to the design calculations of plastic products, but also to the gate design of molds. Please ensure the selection of the correct gating system and the number and location of main channels. The different types and positions of gates can have a significant impact on the quality of the product.
The selection of gate position determines the following characteristics of plastic products:
1. It is a filling behavior;
2. It is the size (tolerance) of the product;
3. It is a contraction action, twisting;
4. It is the level of machine performance;
5. It is the surface quality (appearance).
If the designer chooses the wrong gate, the results are rarely modified in optimizing processing parameters during molding. Therefore, design engineers fully consider the location of the gate.
What is the test mold for Guangdong plastic mold steel
Experimental molds, also known as soft molds or low-cost molds, provide prefabricated components that meet the requirements of mayor/market research, manufacturing assembly, and size related important performance. It provides designers with the opportunity to evaluate uncommon features. All casting and electroplating processes inherently require replicable Guangdong plastic molds, and the quality and durability of Guangdong plastic molds depend on the processing process.
The production of plastic mold steel in Guangdong is less than 100, while other molds can reach several. The method used determines the project cost and time. Important mold data can be obtained from Guangdong plastic mold steel, which can be officially used for mold production in the future. However, the thermal properties and other characteristics of Guangdong plastic mold steel are often different from those of production molds, so it cannot be expected that the processing parameters and manufacturing performance will be completely consistent with the actual production situation.
Do you know what testing molds on plastic molds is now? I hope the above content is helpful to everyone.
Injection molding in injection molding factories is a processing method used for mass production of complex parts with specific shapes. Especially refers to injecting heated and melted materials into the mold cavity under high pressure, and obtaining molded products after cooling and solidification.
How to adjust the temperature in the injection molding factory?
1. The temperature, nozzle temperature, mold temperature, etc. that need to be controlled during the injection molding process in the injection molding factory. The first two temperatures mainly affect the plasticization and flow of plastics, while the next temperature mainly affects the flow and cooling of plastics. Each type of plastic has a different flow temperature. The source or trademark of the same plastic is different, so the flow temperature and decomposition temperature are different. This is because the average molecular weight and molecular weight distribution are different. The plasticization process and temperature selection of plastic vary depending on the type of syringe used. 2. The nozzle temperature is usually slightly lower than the temperature of 3360, in order to prevent the possible occurrence of "drooling" of molten material in straight through nozzles. The nozzle temperature should not be too low. Otherwise, early solidification of the melt can cause nozzle blockage or early clots to be injected into the mold cavity, affecting the performance of the product. 3. The mold temperature of 3360 has a significant impact on the intrinsic performance and apparent quality of the product. The temperature of the mold depends on whether there is plastic crystallization, the size and structure of the product, performance requirements, and other process conditions (melt temperature, injection speed and pressure, molding cycle, etc.).
How to control the pressure in the injection molding factory?
The pressure during the injection molding process in an injection molding factory includes plasticizing pressure and injection pressure, which directly affect the plasticization of plastics and product quality.
1. Plasticization pressure (back pressure) refers to the pressure exerted on the molten material at the top of the screw during its backward rotation when using a screw type injector. The magnitude of this pressure can be adjusted through the relief valve of the hydraulic system. The magnitude of plasticizing pressure during injection should vary according to the design of the screw, product quality requirements, and the type of plastic. If this situation and the speed of the screw remain unchanged, increasing the plasticizing pressure will increase the shear effect, causing the temperature of the melt to rise, but the plasticizing efficiency will decrease, and the reflux and outflow will increase, resulting in an increase in driving force.
In addition, increasing the plasticizing pressure will make the temperature of the melt uniform, the color tone mixed evenly, and the gas in the melt will be discharged. In general work, the determination of plasticizing pressure should be as low as possible, provided that the product quality is excellent. The specific number depends on the type of plastic used, but usually rarely exceeds 20 kilograms per square centimeter.
2. Injection pressure: Currently, in production, almost all injection machines use injection pressure based on the pressure applied by the top plastic of the piston or screw (converted to Euro pressure). The role of injection pressure in injection molding is to overcome the flow resistance of plastic towards the mold cavity, provide the speed for filling the melt, and compress the melt.
Injection molding of plastic molds is a compact tool with a messy shape that can withstand the expansion force of the blank. Therefore, there are high requirements for structural strength, stiffness, general hardness, general roughness, and machining accuracy. The increase in plastic molds for injection molding is one of the important signs of mechanical manufacturing, with long cycles and high processing costs, especially for compact and messy plastic molds or large plastic molds.
Injection molding: What are the main tools used for plastic molds
After long-term operation, the plastic mold becomes sharp, and the sharp blades cannot be magnetized due to demagnetization, otherwise it is easy to cause blockage. Plastic mold companies should keep detailed records of their operations, maintenance (lubrication, cleaning, rust prevention), and environmental damage, and provide information based on the damaged parts and degree of wear for search and use. The data and molding process parameters of plastic molds and materials used in products can shorten the trial operation time of plastic molds and improve cross production efficiency.
Combination plastic molds consist of compression molding, extrusion molding, injection molding, blow molding, and low foaming. Plastic molds mainly include cavities that are combined with the bottom plate of the concave mold, as well as clamping plates that are combined with the concave mold components and concave molds. The concave die is a variable core punch, consisting of a punch combination base plate, punch components, punch combination clamping plate, cavity cutting components, and side cutting combination plate.
Through the coordinated changes of punches, molds, and auxiliary molding systems, a series of plastic parts with different shapes and sizes can be processed. In the plastic processing industry, it is used in conjunction with plastic molding machines to provide complete equipment and tools for plastic products. Due to the diversity of plastics and processing methods, as well as the messy and simple structure of plastic molding machines and plastic products, Dongguan has various types and structures of plastic molds
Injection molding: Precautions in plastic mold processing
1. The plastic molds produced meet the customer's standards, and those with drawings are strictly produced according to the drawing requirements. The processing accuracy of injection molds should be improved as much as possible to make customers more satisfied.
2. Pay attention to timely completion of customer production requirements and do not delay delivery. On the contrary, efforts should be made to achieve rapid response, rapid production, and rapid delivery as much as possible.
3. Pay attention to the maintenance of plastic molds, especially the maintenance of the outer surface of the mold blank, without defects, dust, rust, etc. And keep it clean.
After the plastic mold processing is completed, pay attention to the maintenance of the plastic mold. Clean and maintain the cleanliness of the mold surface.
When handing over and accepting plastic molds, they should be inspected item by item according to standard procedures and relevant acceptance forms. After passing the acceptance inspection, the mold can be packaged and removed.
6. All plastic molds are made with clear materials during production. There is a list of material quality certificates, and some special materials require reports on relevant processing parameters. If there are reports of heat treatment on some dura mater, the processing of injection molds will be twice as efficient.
7. Any inner film or mold parts in plastic molds must strictly follow the production process during processing, and welding or polishing is not allowed without permission.
8. Add exhaust slots at appropriate locations around plastic mold products, and the specifications of the exhaust slots should strictly follow the requirements and standards of the mold designer.
If it is necessary to engrave characters on plastic molds, it is necessary to ensure that all characters are neat and correct, and must not be crooked or twisted.
With the increasing demand for mold quality, precision, and surface complexity in the manufacturing industry, major Dongguan plastic mold factories have higher requirements for their own mold designers. In this context, it is necessary for mold designers to participate in mold design training courses, especially with the popularization of UG mold design and the update of UG software. It is very necessary for mold designers to participate in UG mold design training courses.
On the one hand, in response to the requirements of their own mold factory, mold designers must find ways to improve their mold design capabilities in order to design more competitive plastic molds that meet the needs of various customers for various forms of plastic molds.
On the other hand, only by constantly enriching themselves can mold designers improve their level of plastic mold design and design more precise, high-quality, and complex plastic molds that meet customer requirements.
On the other hand, with the continuous development of the mold design industry, if mold designers do not study hard, it will be difficult for them to find survival space in the industry competition, and elimination is inevitable.
So, whether it's the requirements of customers, plastic mold factories, or to improve themselves, mold designers should actively participate in UG mold training courses. (Guardian Lun)
Stamping molds come in various forms, and automotive mold manufacturers will tell you how to classify them. Stamping molds are also classified based on their working characteristics, mold structure, and mold materials.
One Automobile mold manufacturers classify based on the degree of process combination
A. Single process punching die: A punching die that completes only one stamping process in one stroke of a press.
Composite mold: A mold in which only one station and two or more stamping processes are completed at the same station during one stroke of a press.
C. Progressive die (also known as continuous die): A mold with two or more workstations in the direction of billet feed, in which two or more stamping processes are sequentially completed at different workstations during one stroke of the press.
2、 Automobile mold manufacturers classify according to the processing methods of mold products
According to different processing methods, molds can be divided into five categories: stamping and shearing molds, bending molds, stretching molds, forming molds, and compression molds.
A. Punching and shearing dies: The work is completed through shearing action, and commonly used forms include cutting dies, cutting dies, punching dies, edge cutting dies, edge trimming dies, hole drawing dies, and punching dies.
B. Bending mold: The flat billet is bent into an angle shape. There are many different types of molds based on the shape, accuracy, and output of the parts, such as ordinary bending molds, cam bending molds, curling molds, arc-shaped bending molds, bending stamping molds, and twisting molds.
C. Stretching die: A stretching die is a seamless container made from a flat billet with a bottom.
D. Forming mold: Various local deformation methods are used to change the shape of the blank, including bulging mold, rolling edge forming mold, necking forming mold, hole flange forming mold, and round edge forming mold.
E. Die pressing: It uses strong pressure to make the metal blank flow and deform into the desired shape, and its types include extrusion die, embossing die, stamping die, and end press die.
Plastic mold is the abbreviation for prefabricated plastic molds used for compression molding, extrusion molding, injection molding, blow molding, and low foaming molding. Mainly composed of concave composite substrate, concave composite substrate and concave composite, concave composite substrate with variable cavity composed of card board, convex composite substrate, convex composite card board, cavity cutting unit and side cutting composite board, it can process a series of molded products with different shapes and sizes through the coordinated changes of convex mold, concave mold and auxiliary molding system. So, let's learn about the structure and composition of Guangdong plastic molds together! In order to improve the performance of plastics, various auxiliary materials such as fillers, plasticizers, lubricants, stabilizers, and colorants are added to polymers to make them high-performance plastics.
1. Synthetic resin is the main component of plastics, and its content in plastics is generally 40% to 100%. High content, the properties of resin often determine the properties of plastic, so resin is often considered synonymous with plastic. For example, mixing polyvinyl chloride resin with polyvinyl chloride plastic, phenolic resin with phenolic plastic. Actually, resin and plastic are two different concepts.
Resin is an unprocessed raw polymer that is not only used in the manufacture of plastics, but also as a raw material for coatings, adhesives, and synthetic fibers. On the other hand, apart from a small portion containing 100% resin, most plastics require the addition of other substances in addition to the main component resin.
2. Fillers, also known as fillers, can improve the strength and heat resistance of plastics and reduce costs. For example, adding wood powder to phenolic resin can significantly reduce costs, making phenolic plastic one of the cheapest plastics while significantly improving mechanical strength. There are two types of fillers: organic fillers and inorganic fillers. The former includes wood powder, shredded cloth, paper, various textile fibers, etc., while the latter includes glass fiber, diatomaceous earth, asbestos, carbon black, etc.
3. Plasticizers increase the plasticity and flexibility of plastics, reduce brittleness, and facilitate the processing and shaping of plastics. Plasticizers are generally mixed with resins and are non-toxic, odorless, heat-resistant and stable high boiling organic compounds. Phthalates are commonly used. For example, when manufacturing polyvinyl chloride plastic, adding more plasticizers can obtain soft polyvinyl chloride plastic, but without adding plasticizers or reducing the amount added.
4. Stabilizers are added to plastics to prevent the decomposition and damage of synthetic resins caused by light and heat during processing and use, and to extend their lifespan. Commonly used ones include stearic acid salts, epoxy resins, etc.
5. Colorants can give plastics various bright and beautiful colors. As coloring agents, organic dyes and inorganic pigments are often used.
6. The function of lubricants is to prevent plastic from sticking to the mold during molding, while also making the plastic surface smooth and aesthetically pleasing. Common lubricants include stearic acid and its calcium magnesium salts. In addition to the above-mentioned additives, flame retardants, foaming agents, anti-static agents, etc. can also be added to plastics.
Guangdong plastic mold forming is a processing method used for mass production of complex shaped parts. The specific principle is to use the screw of the injection molding machine to push high pressure, place the melted plastic material into the cavity of the plastic mold, cool and solidify, and obtain the plastic molded product.
The above introduction is about the structure and composition of Guangdong plastic molds. Plastic molds consist of two parts: a moving mold and a fixed mold. The moving mold is installed on the moving template of the injection molding machine, and the fixed mold is installed on the fixed template of the injection molding machine. During injection molding, the moving and fixed molds are closed to form a pouring system and chamber. When opening the mold, the moving and fixed molds are separated to remove the plastic product.
Hot runner has become indispensable in injection molding production. For plastic processing enterprises, choosing a hot runner suitable for product molding and mastering the correct use of hot runners are the key to benefiting from hot runners. So, let's learn about the role of hot runners in Dongguan plastic mold design together!
Hot runner (HRS), also known as soup mouth, transforms the solidified spout into a molten spout. Its composition is relatively simple. Dongguan plastic molds mainly include splitter plates, hot nozzles, temperature controllers, etc. Among them, the splitter plate can be divided into I-shaped, X-shaped, Y-shaped, T-shaped, mouth shaped, and other special shapes according to its shape; Hot nozzles are divided into large nozzles, front-end nozzles, and needle valve nozzles according to their shapes; Thermostats are divided into clock core type, box type, and computer centralized control type according to temperature regulation methods.
In the processing of plastic molds in Dongguan, the combination of hot runners and molds plays a very important role. For example, in the injection production of ultra-thin components such as mobile phone battery covers, for injection materials with poor flowability that can easily produce high-precision and high-quality products through the use of hot runners, such as LCP, the flowability of the raw materials can be significantly improved, ensuring smooth injection production. For large injection molded products such as car bumpers, door panels, TV rear covers, and air conditioning cases, the use of hot runners can make very difficult injection molding relatively simple.
In multi cavity mold injection molding, if the hot runner is insufficient, it cannot be molded. Hot runner can be said to be a technology that ensures the balance of the flow channel. Due to the shear force of plastic on the flow channel, no matter how much reasonable geometric balance the mold has, the weight of the formed product is difficult to be consistent. Especially in the case of multi cavity molds, if a hot runner is not used, the outer side of the formed product will be lighter than the inner side.
For plastic processing enterprises, as long as there is a certain amount of injection molding production, using hot runners is quite economical. This is because hot runners help companies eliminate water outlets through injection molding production. In most cases, the water outlet cannot be reused. Sometimes, the weight of the nozzle is similar to that of the product. If traditional nozzle injection method is used, it means that there are useless raw materials like those used in the product. It is estimated that using a hot runner can save 30% to 50% of raw materials.
In addition, hot runners also help reduce mold wear and extend the lifespan of the mold. Generally speaking, the lifespan of hot runner molds is twice that of fine nozzle molds.
The structure of a hot runner is relatively simple, but its various components play important roles. Usually, high-quality hot runners have high requirements for structural design and materials. Regarding the sharp hot runner, all the heaters and temperature sensing wires used are imported from South Korea, and the steel used is imported from Japan. These are the prerequisites for ensuring the quality of the hot runner. Hot runner suppliers should also assist customers in designing and installing suitable hot runner systems based on their plastic products and the molds used.
When using PP material for door panels, a Y-shaped splitter plate and three hot nozzles with three-point hot flow channels are usually used. This solution greatly reduces manufacturing costs while ensuring product forming quality; When using fire-resistant ABS material for door panels, in order to ensure the smooth formation of the product, special splitter plates and 5 hot runners with 5 hot nozzles are required.
The above introduction is about the role of hot runner in Dongguan plastic mold design. If you need to learn more, please feel free to contact us at any time!

Plastic is a material mainly composed of high mole...
Plastic is a material mainly c...
Precautions for using hot runn...
Dongguan plastic mold is a com...

Plastic is a materia...

Precautions for using hot runner system in Guangdo...
Plastic is a material mainly c...
Precautions for using hot runn...
Dongguan plastic mold is a com...

Precautions for usin...

Dongguan plastic mold is a compact tool that has a...
Plastic is a material mainly c...
Precautions for using hot runn...
Dongguan plastic mold is a com...

Dongguan plastic mol...

The choice of plastic mold steel in Guangdong is t...
Plastic is a material mainly c...
Precautions for using hot runn...
Dongguan plastic mold is a com...

The choice of plasti...

Injection molding in injection molding factories i...
Plastic is a material mainly c...
Precautions for using hot runn...
Dongguan plastic mold is a com...

Injection molding in...

Injection molding of plastic molds is a compact to...
Plastic is a material mainly c...
Precautions for using hot runn...
Dongguan plastic mold is a com...

Injection molding of...

With the increasing demand for mold quality, preci...
Plastic is a material mainly c...
Precautions for using hot runn...
Dongguan plastic mold is a com...

With the increasing ...

Stamping molds come in various forms, and automoti...
Plastic is a material mainly c...
Precautions for using hot runn...
Dongguan plastic mold is a com...

Stamping molds come ...

Plastic mold is the abbreviation for prefabricated...
Plastic is a material mainly c...
Precautions for using hot runn...
Dongguan plastic mold is a com...

Plastic mold is the ...

Hot runner has become indispensable in injection m...
Plastic is a material mainly c...
Precautions for using hot runn...
Dongguan plastic mold is a com...

Hot runner has becom...